
The catalytic converter was one of the greatest emission control inventions in the history of monitoring carbon and greenhouse gas emissions. It starts in the engine, but the catalytic converter is the last stop for exhaust gases and the last chance to launder that nasty air before it shoots into the atmosphere, and our noses.
How It Works? Basically, Your catalytic converter is a magical hot box. Ok, it's not magic, but it sounds magical the first time you hear how it works. Hot exhaust gases exit your engine and head through your exhaust to the catalytic converter. Inside this expanded tube is a massive network or honeycomb of ceramics. This ceramic checkpoint has been coated with compounds that react with the exhaust to eliminate certain harmful emissions. Even though the exhaust is flying through the tube at high velocity, the molecules that coat the ceramics are able to react in milliseconds, hanging on to the bad stuff until it's converted to something harmless (or less harmful) like Nitrogen, Carbon Dioxide or water vapor.
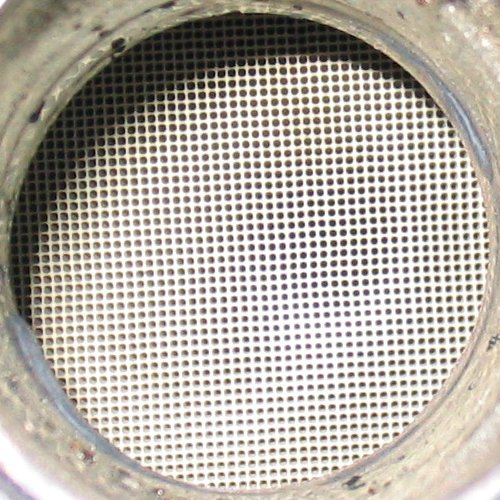
There are a number of factors that affect the performance of your catalytic converter. The converter works in conjunction with your oxygen sensors to come up with the cleanest possible exhaust. As long as everything is operating as it should - engine at proper operating temp, air/fuel mixture optimized, no contaminants added to the exhaust - the system works really well. Throw a faulty O2 sensor into the mix and you have problems. Since the O2 sensor can alter your air/fuel mixture, it can kill your catalytic converter. If the mix is too lean, the converter won't have the right elements to clean the exhaust. Too rich and the converter will heat up to the point of melting, and trying to push exhaust through a solid block is tough. If your car burns oil or leaks coolant into the engine, these contaminants can collect on the ceramics inside the converter and cause it to clog.
There are many things that can make inoperable or ruin your catalytic converter, but keeping your car well tuned and in top repair will give you a lifetime of emission control.
Now that you know the basic function of a catalytic converter, you can pop some popcorn and rip into your new NetFlix package. But if you're still thirsty for science, here's what happens on the inside of that steel cylinder under your car. Once your catalytic converter reaches its operating temperature (known as "light off temperature" and usually between 400 and 600 degrees Fahrenheit) the catalyst compound coating the inner ceramics start to convert the three regulated harmful emissions into less harmful emissions. The three harmful emissions regulated by the EPA are Carbon monoxide (CO), Hydrocarbons (or VOCs for Volatile Organic Compounds), and Nitrogen compounds (NOx).

IMT-610N Injector Cleaner is an advanced electromechanical product, which can clean and test injectors by simulating engine...
Award winning Unique technology with dual monitors that fits alignment on all platform including 2 post...